JWT (JSON Web Token)
JWT Definition :
A JSON web token(JWT) or (“jot”) is JSON Object used to securely transfer data over the web. It is mostly used for sending authentication data.
JWT Need:
1) Everything going stateless
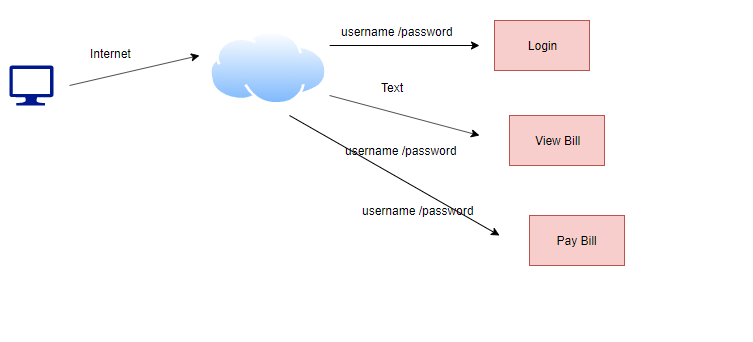
Consider the below situation, where we have REST APIs to provide data to the user. Firstly, a user logs in and we send the username password to the login API and it gets authenticated by looking up details in the database or LDAP.
These REST APIs are stateless so they don’t maintain session or knowledge if the user is authenticated in previous flows.
So next time, if user clicks on view bill and it calls view bill API, we need to pass username and password again for re-authentication.
So this will make all APIs to re-authenticate against database/LDAP for each call.
2) Need to provide scalability.
We often use load balancers to cater to needs for high traffic and high availability. Now imagine, if we are maintaining user session at server level, then also it makes it complex to scale.
For example, we may have 2 servers behind the load balancer and say it hits the server1 and get authenticated. In the next hit, if we go to server 2, which is not having any session data,
it will throw an error since no user information is available.
JWT Usage :
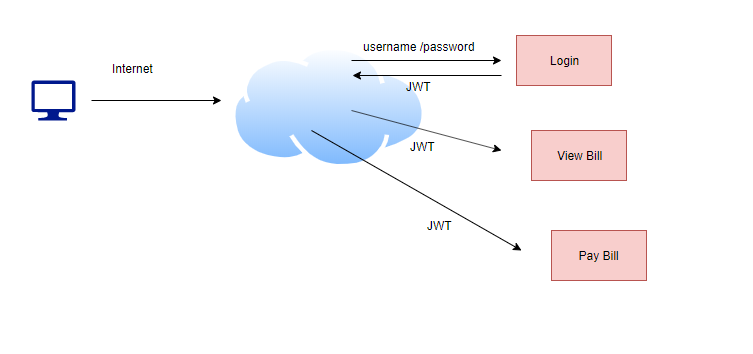
Let’s see JWT in action. User logs in and provides username, password and it gets authenticated. The authentication server will create a JWT token and send it back to the user.
Now the user will make other calls and sends back the JWT token to the server again. The authentication server will validate the token and then allow the calls to the APIs.
So this time, the user is not providing session-id or credentials, but this JWT token to the server.
JWT elements :
JWT token is a long base 64 encoded string. If we decode it, we can see it as a JSON object.
The decoded token consists of :
– header: Mainly has the signing algorithm information
– payload: Mainly some user details, like user id, name, username
– signature: a hash by combining header and payload
The token is formatted as header.payload.signature
Header :
{
“typ”:”JWT”,
“alg”:”HS256″
}
It consists of an algorithm and type details. The most popular algorithms are HS256 and RS256. If the server doesn’t want any encryption, it can also put “none” for the algorithm.
Payload :
{
“userId”:”776571263-ef”,
“name”: “Jason”,
“admin”: true,
“iss”: “https://sampleweb.com/”,
“sub”: “auth/some-hash-here”,
“exp”: 76782366
}
Payload has all user data information which is also called “claims” of the JWT.
As it is readable, we should not put any sensitive or PI data into this token. There are no mandatory fields and applications can have their own sets.
Signature :
This is used to verify or authenticate the token. So basically, BASE64URL encoded header and payload are joined together with dot(.) and then they are hashed using the algorithm mentioned in header with a secret key.
This is then appended to header and payload using dot(.)
So it will be like : HASHINGALGO( base64UrlEncode(header) + “.” + base64UrlEncode(payload),secret)
Sample JWT Example code (Java)
There are many libraries available for JWT and in this example, I am using jjwt
We can either download it from git or add maven dependencies as below in pom file.
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-api</artifactId>
<version>0.10.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-impl</artifactId>
<version>0.10.7</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-jackson</artifactId>
<version>0.10.7</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
Sample Code : Refer : https://www.jsonwebtoken.io/