SQL
SQL : Structured query language that help us to access or manipulate data from the database. We can CREATE, UPDATE, DELETE and retrieve data while using SQL.
RDBMS : Relational Database Management System. It is the basis of SQL. It is for modern data base systems like MySQL, Oracle. In RDBMS the data is stored in the forms of tables and the collection of data related to the entries are saved in the forms of columns and rows.Each table is broken up into smaller entities called fields.
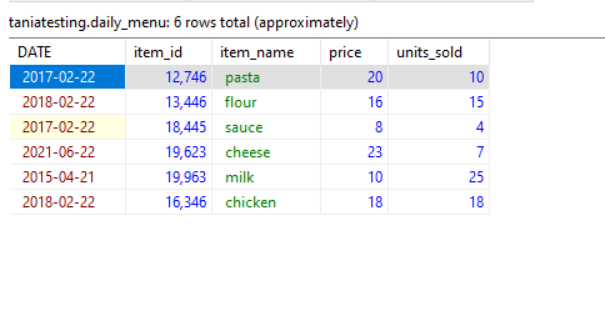
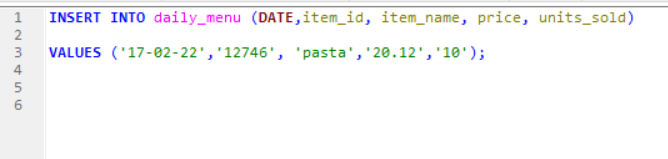
In the below picture: table name is daily_menu. The fields in the Customers table consists of date, item_id, item_name , price and units_sold.
A field is a column in a table which is mainly designed for the specific information about every record in the table.
The Rows, define an individual entry that exists in the table. Row, also called as record defines the horizontal entity in the table. Whereas column is a vertical entity in the table which contains all the information related to the specific field in the table.
For example::
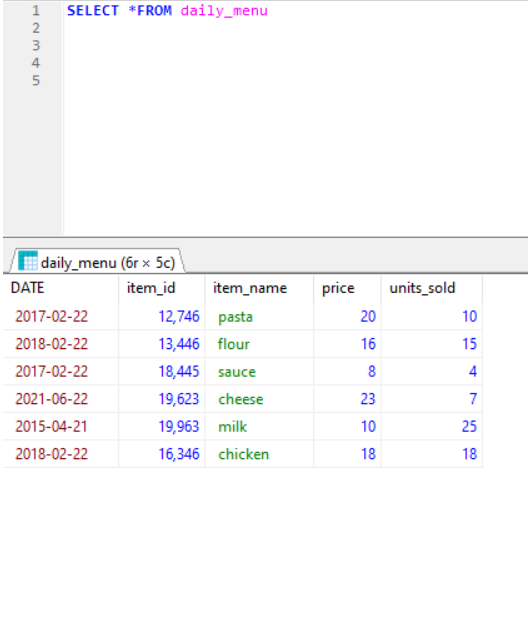
The table (daily_menu) below contains six records and five columns (date, item_id, item_name , price, units_sold).
SQL Statements/ Syntax:
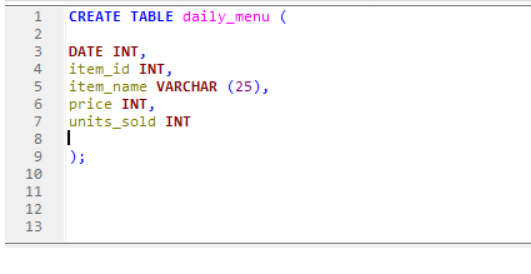
CREATE : command which helps to create a table .
Example: As shown below we created a table named daily_menu, and add fields (columns) in the table.
INSERT INTO: command which helps to add data in the table .
Example: we add data in the table daily _menu below while using command Insert into.
SELECT: command which select all the records from the table.
e.g : SELECT * FROM Table( * select all )
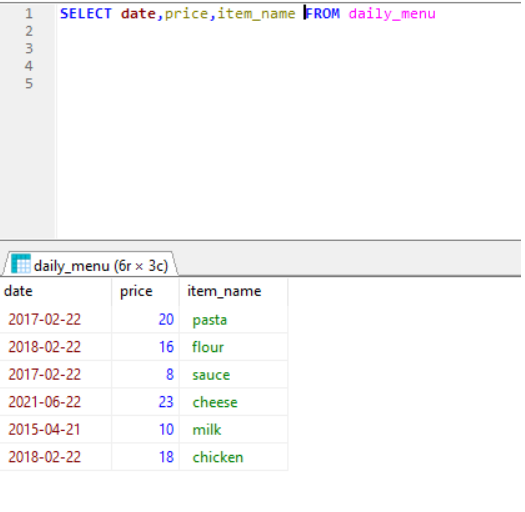
or SELECT date, price , item_name FROM daily_menu; ( when need specific column record use column name instead of *)
3) SELECT DISTINCT: command used to return different values. In a table,sometimes column contains many duplicate values
and we only want to list different (distinct) values, that time we use SELECT DISTINCT command.
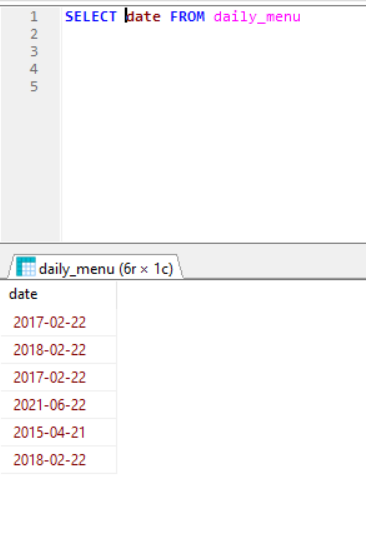
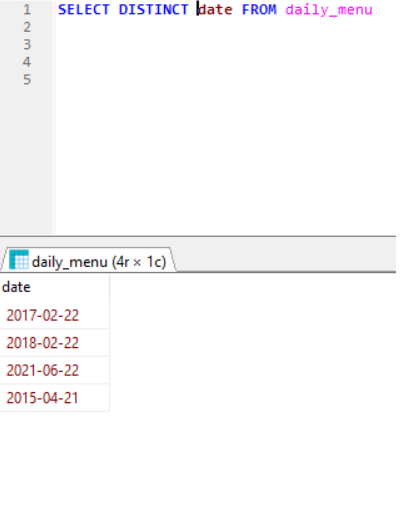
e.g: SELECT date FROM daily_menu (Select all the dates from the table including duplicate dates as well)
SELECT DISTINCT date FROM daily_menu (Select only the distinct values{remove duplicate}from “date” column in the “daily_menu” table
_
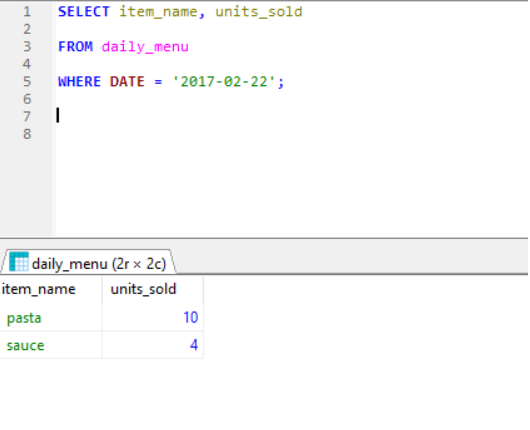
WHERE- Clause used to filter records. It extract only those records that fulfils a particular condition. We can use WHERE clause in UPDATE, DELETE conditions as well .
For example:
Below mentioned operators we can use with the Where clause:
-
= equal
- > gretaer than
- < less than
- >=gretaer than or equal
- <= less than or equal
- <>not equal , != also called not equal
- BETWEEN (mention certain range)
- LIKE
-
IN (multiple possible value)
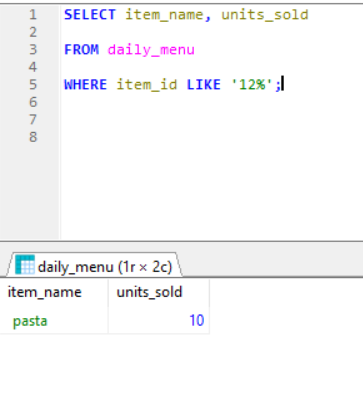
Below table shows example of using LIKE Clause.
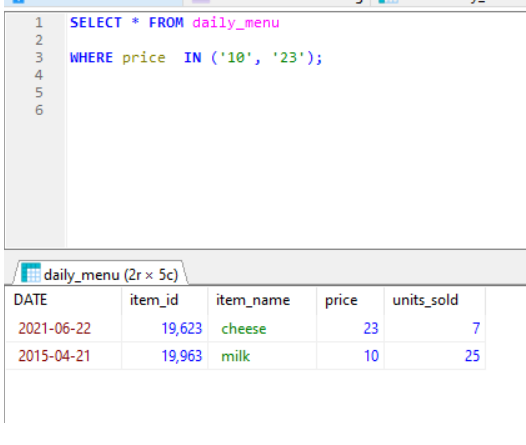
Below table shows example of using IN Clause.
AND, OR , NOT Clause:
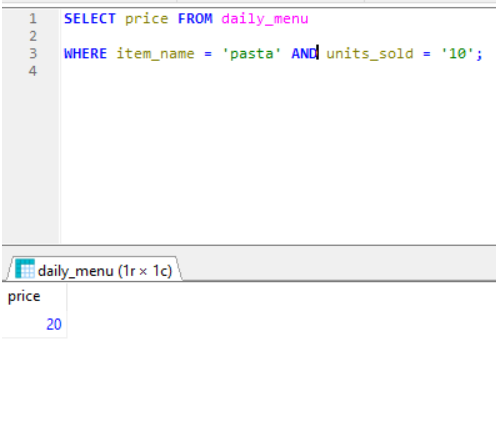
AND- displays record if all conditions are True and separated by AND
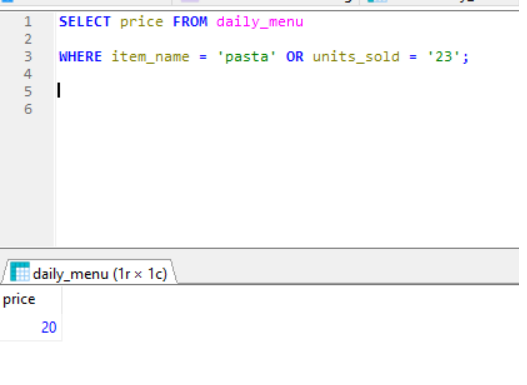
OR- displays record if any of the condition is True and seperated by OR
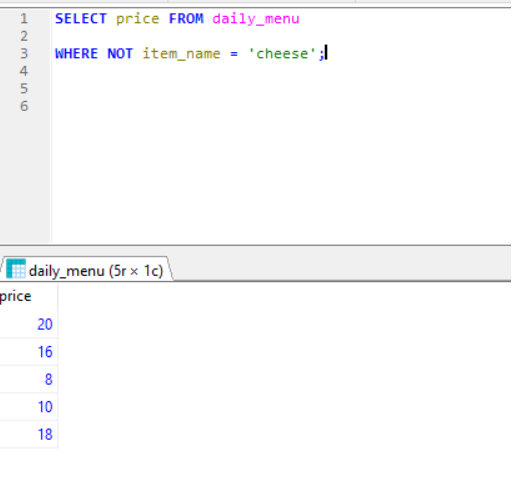
NOT- Displays a record if the condition (s) is NOT True.
AND-
OR-
NOT-
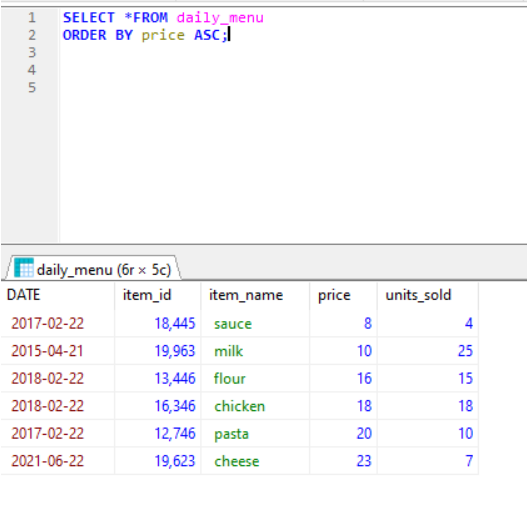
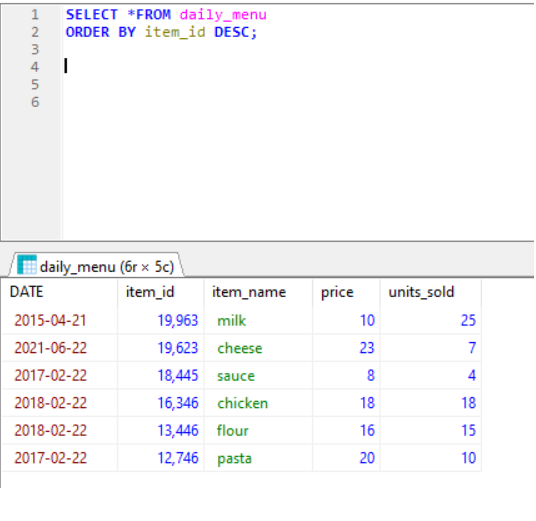
ORDER BY- used when we need to fetch dta in an order like in Ascending or descending order.
Example ORDER by DESC
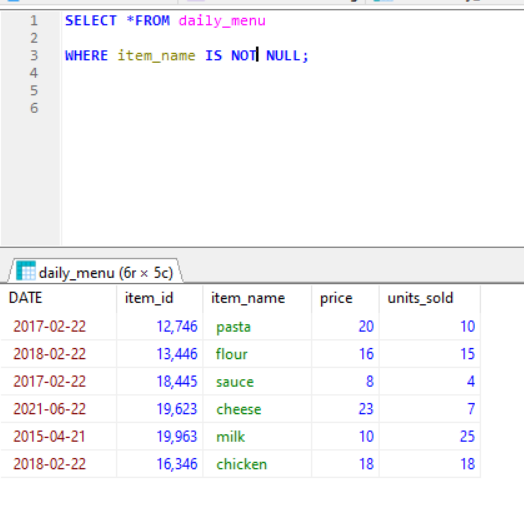
NULL Values: Null value is defined a field that has no value, it is different from zero value or field that contain space. Null value is the one which we generally left blank during creating a record. WE have to use IS NULL and IS NOT NULL operations.

Example IS NOT NULL-
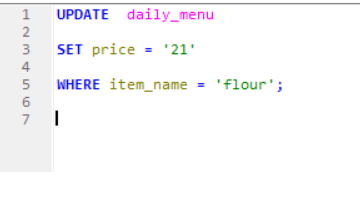
UPDATE: We use Update command when we need to modify the existing record
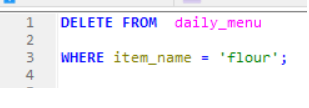
DELETE- Used to delete the existing record

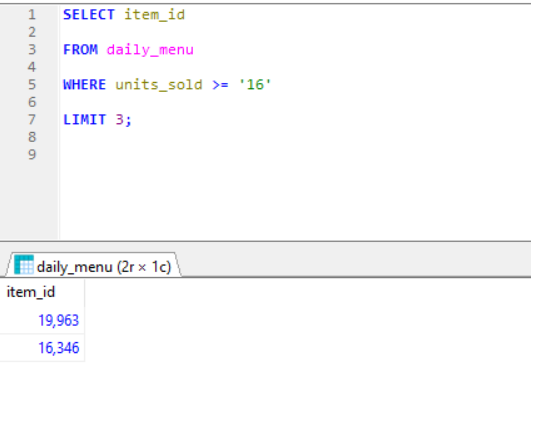
SELECT TOP, LIMIT, FETCH FIRST and ROWNUM clause:
- All database doesn’t support SELECT TOP clause, therefore if we are using My SQL then we need to use LIMIT clause to fetch the data and In case of Oracle we need to use clause FETCH FIRST and ROWNUM clause.
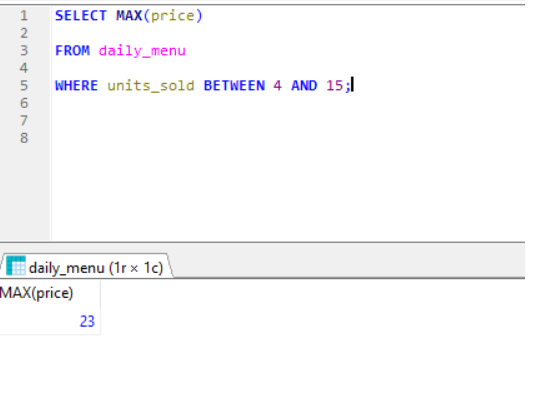
MIN and MAX-
Returns the smallest and largest value of the selected column.
SQL Join:
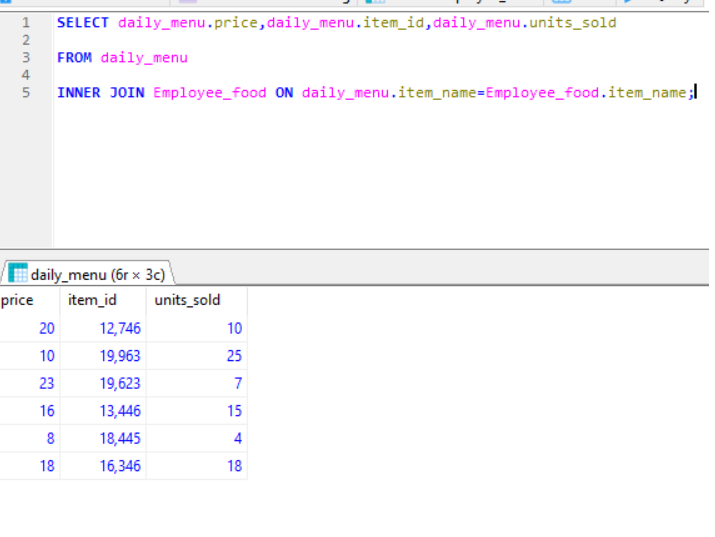
Join clause is used when we need to combine two or more tables, based on a related column between them.
Syntax for join/inner join:
Select column_name from table 1 Inner join table 2 ON table1.column_name= table2.column_name;
Left JOIN– returns all records from the left table (table 1) and matching record from the right table (table 2). If there is no matching record on the right table,the result is zero from the right table.
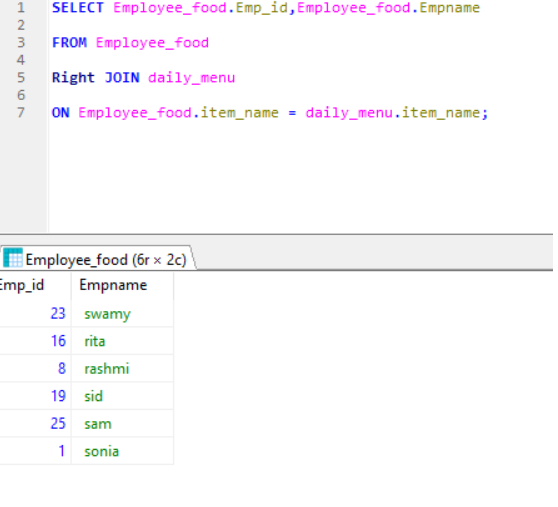
*In the below example , Employee_food (table 1) and daily_menu (table 2). Both tables have item_name common Column.
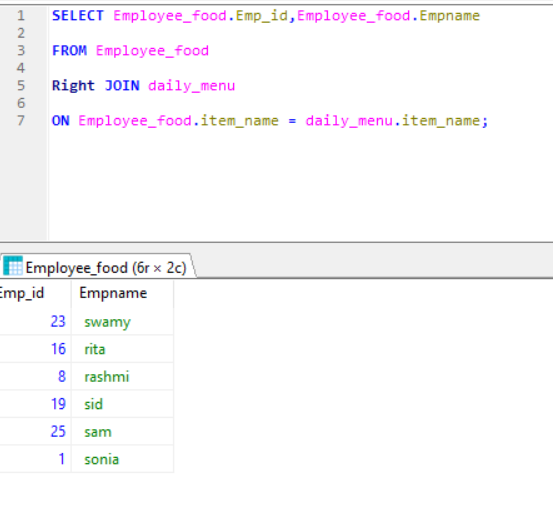
Right JOIN– Fetch all records from the right table and matching record from the left table.